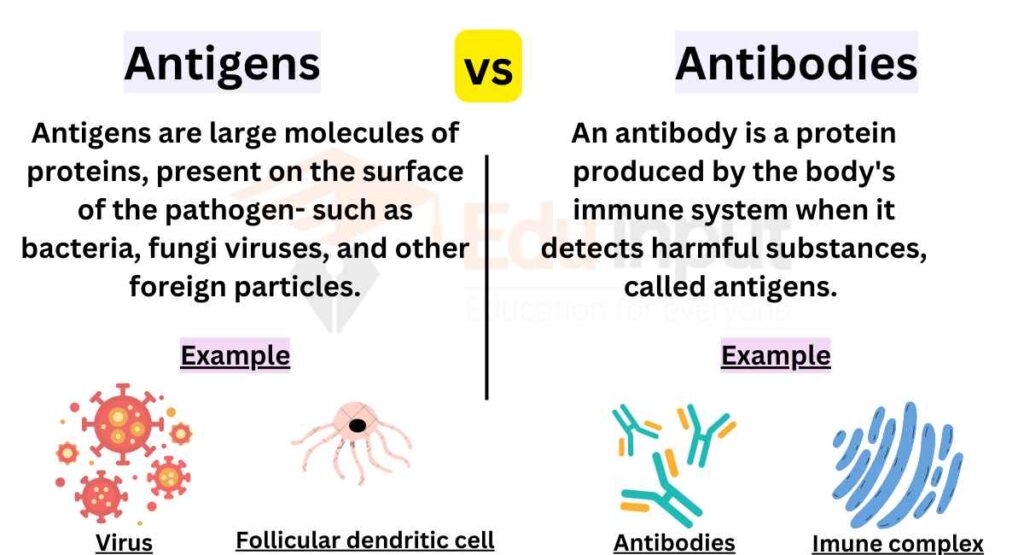
Antigen Definition Physiology . an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. Any foreign invaders, such as. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen.
from eduinput.com
an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. Any foreign invaders, such as. the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies.
Differences Between Antigens And Antibodies
Antigen Definition Physiology the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. Any foreign invaders, such as. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the.
From www.studocu.com
Difference Between T Cell Dependent and Independent Antigen 1 Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. any. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From teachmephysiology.com
Antigen Processing and Presentation TeachMePhysiology Antigen Definition Physiology Any foreign invaders, such as. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. an antigen is a molecule that initiates. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From sciencenotes.org
Antigen Definition, Function, and Types Antigen Definition Physiology any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. Any foreign invaders, such as. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.savemyexams.com
Human Defence Systems AQA GCSE Biology Revision Notes 2018 Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. Any foreign invaders,. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From exotsbftl.blob.core.windows.net
Antigen And Antibody Modeling at Susan Wesley blog Antigen Definition Physiology any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. antigen, substance. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From universe84a.com
Antigen Definition, Types, Factor Affecting Antigenicity, Adjuvant Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. Any foreign invaders, such as. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From support.10xgenomics.com
Antigen Capture or Barcode Enabled Antigen Mapping (BEAM) with Cell Antigen Definition Physiology the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Antigen Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Antigen Definition Physiology Any foreign invaders, such as. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. . Antigen Definition Physiology.
From eduinput.com
Differences Between Antigens And Antibodies Antigen Definition Physiology any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. antigen, substance. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.animalia-life.club
Immune Response Graph Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. Any foreign invaders, such as. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From en.ppt-online.org
Antigenantibody reactions and selected tests online presentation Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. the antigen acts as an antibody generator, and it gets eliminated (along with the infectious agent or the cancer cell) by the body's. . Antigen Definition Physiology.
From exoueexic.blob.core.windows.net
Antibody Definition Animal at Tammy Archibald blog Antigen Definition Physiology any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. an antigen is a molecule. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.youtube.com
O antigen and H antigen Definition and 21 Key Differences YouTube Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. any. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Adaptive Immune Response T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. an antigen. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Antigen and Antibody PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Antigen Definition Physiology any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. Any foreign invaders, such as. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. antigen, substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response, specifically activating lymphocytes, which. an antigen is a. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.pinterest.com
Binding of antibodies to antigenseffector mechanisms Immune system Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers an immune response because the. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From socratic.org
How many possible blood antigen combinations are there? Socratic Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a molecule or particle, often found on the surface of cells, viruses, or bacteria, that triggers. Antigen Definition Physiology.
From www.pdfprof.com
antigène définition Antigen Definition Physiology an antigen is a molecule that initiates the production of an antibody and causes an immune response. an antigen is a large protein molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the body by the production of antibodies. any substance that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. an antigen. Antigen Definition Physiology.